Osteoporosis
What is Osteoporosis?
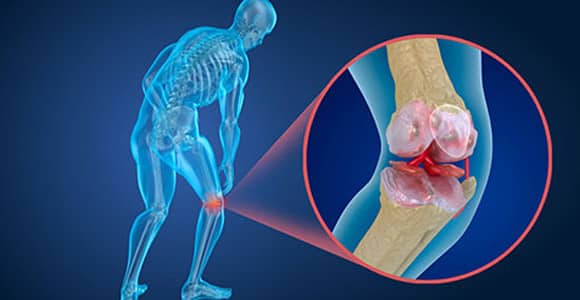
Osteoporosis literally means pores (or holes) in bones. It is a bone disease wherein the bone density of the body decreases below the normal for that age. Usually occurring in post-menopausal women, it is further compounded by the fact that at the same time the body produces new bone very sparsely.
Though occurring in both men and women, Osteoporosis is much more common among women after their menopause. This is because, with menopause, oestrogen (the hormone that primarily prevents bones from erosion) suddenly decreases to a great extent.
As the density of bone is decreased to below normal levels, affected people become prone to fractures, even with the slightest of injuries or falls. Bones around the hips, wrists and the spine are most prone to breakage as they are the weight bearing struts. Smoking and poor diet are other risk factors that increase the risk of osteoporosis and Osteopenia.
Why treat Osteoporosis?
Before osteoporosis sets in (pre-menopause), the aim is to build bone mass and slow down bone erosion.
Once osteoporosis sets in, treatment is aimed at
- Maintaining bone mass
- Reducing bone and muscle aches and pains
- Improving quality of life
- Preventing fractures following simple falls
How and what type of drugs can help in Osteoporosis?
The treatment of osteoporosis is multi-pronged, and involves a combination of lifestyle modification, good nutritious diet, regular exercise and medication. Drugs used today include:
- Anti-resorptive drugs: most used medication, aimed at preventing further bone erosion, and thereby indirectly improving bone strength.
- RANKL inhibitors like denosumab (Xgeva), which works as a general anti resorptive as well as an immune therapy for osteopathic diseases
- Estrogen agonists or selective estrogen-receptor modulators (Raloxifene, Toremifene, Tamoxifen), used around menopause (to restore estrogen levels needed for bone production).
- Parathyroid hormone analogues (Teriparatide), which is the only true drug that stimulates new bone formation.
- Calcitonin (Miacalcin, Calcimar) specifically Signs and symptoms of Osteoporosis
In most cases, Osteoporosis is silent disease (symptomless) and takes many years to reach a point where clinical attention is sought. Most of the people do not even understand that they are suffering from Osteoporosis till they actually suffer from a fracture with the slightest of injuries or falls. The condition may sometimes worsen to a level where a fracture can happen even from sneezing or coughing. If these fractures occur in the spine, a permanent change in the posture can be noticed.
What causes osteoporosis and risk factors
The causes of Osteoporosis can be divided into 2 groups:
Unavoidable or Non-modifiable factors
- Age (technically, after the age of 30, bone density cannot increase, so the aim is to maintain the levels of bone mass)
- Ethnicity (Asians and Caucasians are most prone)
- Lower Estrogen level (as in early menopause, or post-uterus and ovary removal)
- Genetic factors (family history of osteoporosis or fractures following simple falls)
- Poor bony and physical structure
- Past history of fractures following simple falls/injury (People aged 50 years and above with a previous history of fractures)
Modifiable risk factors
- Inadequate diet (Low intake of vitamin D, calcium and magnesium)
- Malabsorption problems
- Excessive intake of alcohol
- Tobacco consumption (oral/smoking)
- Prolonged inactivity or immobility (years)
- Diseases like hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism and Cushing’s disease (all affect the hormone levels that regulate healthy bones and lower bone density)
Other risk factors of Osteoporosis
The other risk factors include:
- COPD
- Cancer
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (inflammatory arthritis in large joints and spine)
- Rheumatoid arthritis (a chronic inflammatory disorder in joints, hands and feet)
- Chronic kidney disease
Medications which can increase the risk of Osteoporosis
There are certain medicines and health conditions which can worsen Osteoporosis:
- Corticosteroids and Glucocorticoids (steroid hormones)
- vitamin A (retinoids)
- Blood-thinners
- Antidepressant medication
- Thiazolidinediones (type 2 diabetes medicines)
- Thyroid hormone
- Antacids that mess with mineral status (PPIs)
- Aromatase inhibitors (breast cancer and gynecomastia treatment)
- Thiazide diuretics (hypertension and edema medicines)
- Cancer medicines (chemotherapeutic agents)
How to prevent osteoporosis
Calcium and vitamin D are the most essential components of human bones. If a young adult of 19 years or above consumes calcium less than 1000mg/day then he or she is exposed to greater risk of lower bone density after 30 years of age. For women aged >51, the minimum daily intake should be 1,200mg.
Dairy products are the best source of calcium. This list includes:
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Milk, cheese and yogurt
- Soft-boned fish
- Kale, broccoli and other green vegetables
Sources of adequate Vitamin D include:
- Regular and moderate sun exposure
- Saltwater fish
- Fortified foods (Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin D, Iodine, Iron, Folic acid)
- Cheese, Egg yolks
Lifestyle changes that help control bone density
- Quitting smoking can increase the formation of new bone
- Restriction on alcohol consumption
- Weight-bearing exercise with muscle strengthening
- Yoga for enhanced flexibility of the body
All Orthopaedic surgeons recommend regular bone mineral density screening (DEXA scan) especially for women aged 65 years and over.
Content Reviewed By: Dr. Rajeev Thukral
Parkinson’s Disease
What is Parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease is a gradual progressive nervous system disorder that leads to shaking, difficulty with walking, stiffness, balance and coordination. The symptoms start very simplistically with something as trivial as slight trembling in one hand, however the same increases as days go by. Starting from a negligible symptom, Parkinson’s disease cause permanent stiffness or slowing of regular movement.
At the early Parkinson’s disease symptoms, the normal speech of a person can go softer or more broken than usual. There is no distinctive Parkinson’s disease cure. Instead, once someone is affected with this condition, the symptoms are treated with different medications to slow down the aggravation.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease symptoms can largely vary from person to person. At the starting, most of the symptoms are mostly unnoticed. Generally, the symptoms start from one side of the body and aggravate to the other side. Here are few of the most common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease:
Shaking or Tremor: A patient most commonly starts to feel shaky or trembling in his or her hands, fingers or limbs. First, the condition mostly occurs when moving. With time, this condition starts occurring when the patient is in rest as well.
Slowed movement: With the permanent slowed movement of the patient, everyday tasks like moving, responding or doing simple daily tasks become difficult and time-consuming. With aggravation, even getting up from the chair or dragging the feet for walking becomes a tough job.
Impaired posture and balance: Balancing the body posture can be a great point of difficulty for Parkinson’s disease patients. Changing posture can seem almost impossible at the advanced stages.
Rigid muscles:Painful muscle stiffness can happen at any part of the body. This condition can limit the range of motion to a great extend.
Loss of automatic movements: Automatic movements like smiling, blinking and swinging of arms while walking are heavily disrupted.
Changes in speech: Before the patient starts talking, his or her voice either drops or becomes rough. The speech generally loses the depth and fluctuation and become flatter.
Writing changes: Generally, the patient feels difficulty in writing and the handwriting appears smaller.
Causes of Parkinson’s disease
In Parkinson’s disease, Neurons gradually break down or die. In a healthy brain, Neurons produce dopamine, a chemical messenger. When the dopamine level in the brain decreases, the brain starts to behave weirdly.
Though the definitive cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, here are few most plausible factors:
Genes: There are research reports that show Parkinson’s disease originates from specific genetic mutations. But, this condition is pretty rare.
Environmental triggers: Multiple environmental factors or exposure to certain toxins can result in Parkinson’s disease. Chance of happening this is also quite less as well.
When the brains of people with Parkinson’s disease are examined, many changes have been noted. But, scientists are not particularly sure why these changes happen. The changes include:
Lewy bodies: Patients of Parkinson’s disease are found with clumps with some microscopic substances in the blood cells. These substances are named Lewy bodies. Though no concrete evidence is found, scientists believe that these substances have a direct impact on the patient’s performance.
Alpha-synuclein within Lewy bodies: The presence of Alpha-synuclein, a natural and widespread protein in all Lewy bodies do not let the cells to break down.
Risk factors of Parkinson’s disease
Though the definite risk factors are still not established, doctors hold few factors responsible:
Age: People of 60 years of age and more generally experience Parkinson’s disease and young people very rarely develop this condition.
Sex: Though researchers have still not been able to figure out the scientific reason; men affected with Parkinson’s disease are more in number than women.
Complications with Parkinson’s disease
Multiple complications often come with Parkinson’s disease but in most of the cases, these complications are treatable.
Difficulty in thinking: Dementia, a social ability symptom that messes with daily activity is one of the most common complications. This symptom generally comes at the advanced stage of Parkinson’s disease. Generally, medications cannot help difficulty thinking to a great extent at this moment.
Mood swings and depression: Depression is a complication that often starts from the early stages of Parkinson’s and remains throughout the lifetime. Generally, depression is treatable to some extent.
Along with depression, all the other human emotions like anger, fear, love, anxiety and loss of motivation are experienced at a high level.
Problem while eating: Especially at the later stages of Parkinson’s disease, patients face moderate to serious problems in chewing foods. As the swallowing process also gets slower, the saliva starts to accumulate in the mouth. Also, as the facial muscles get affected with the slowed-down brain, this chronic condition can lead to poor nutrition and even chocking. This problem also leads to constipation.
Sleep Disorder: People with Parkinson’s disease keep waking up throughout the night; sometimes with inexplicable anxiety as well. This symptom results in sleepiness throughout the day. Some people have reported rapid eye movement while trying to sleep. Generally, all the symptoms are well treatable with medications.
Some medical researchers have proved that drinking caffeine significantly helps in avoiding Parkinson’s disease.
Content Reviewed By: Dr.Kamal Verma
The Prostate Cancer
What is The Prostate Cancer?
The Prostate is a small walnut-shaped gland present in the male body. The Prostate produces a seminal fluid which transports and nourishes the sperm. When there is any abnormality with cell development in the Prostate, it is diagnosed as Prostate Cancer.
The Prostate Cancer is one of the most common cancers among Indian men. At the advanced stages, cancer often spreads from the Prostate to the adjacent body parts as well. The Prostate Cancer, a slow-growing cancer type, often develops within the patient’s body for years. Majority of the Prostate Cancer patients live a normal and asymptomatic life without it becoming life-threatening. The Prostate Cancers which are detected at an early stage and haven’t spread to other organs till then have a greater chance of complete recovery.
The Prostate cancer symptoms
At the early stages, The Prostate Cancer is often asymptomatic. In advanced stages, the signs of the Prostate cancer are:
- Troubled and interrupted urinating
- Need to urinate frequently
- More frequent urge to urinate during the nights
- Decreased amount of fluid ejaculated
- Erectile dysfunction
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood coming out with Semen
- Difficulty in holding back the urine
- Pain and pressure in the rectum
- Pelvic bone pain
- Painful or burning sensation in urination
- Discomfort and pain in the pelvic area
- Pain in pelvis, hips, thighs and lower back
Causes of Prostate Cancer
The definitive cause of the Prostate Cancer is still unknown. Therefore, the cause of this disease is largely determined from the probable risk factors:
- Age Men over 50 years of age are most prone to The Prostate Cancer.
- Family History If the patient’s father or brother had developed the Prostate Cancer before the age of 60, he is at a greater risk of developing the Prostate cancer. Research has also shown that if any female member of the close family has breast cancer, then it increases the chance of the Prostate Cancer.
- Ethnic Group Asian men are least prone to develop the Prostate Cancer in comparison to African and African-Caribbean race.
- Obesity Though there is no full proof evidence but researches have shown that obese people have developed the Prostate Cancer more than non-obese counterpart. Also, healthy diet and regular exercise keep the Prostate Cancer at bay. The research has also shown that people who have taken a high amount of fat and Calcium in their daily diet are more prone to develop the Prostate Cancer.
Detection and Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Generally, The Prostate Cancer is diagnosed by blood tests and physical examinations.
-
- The Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test PSA test is the most authentic blood test for the Prostate Cancer. The result shows whether the Prostate-specific Antigen, the substance responsible for the cancer is within normal range or not. If the PSA level is above the normal range, then an MRI scan of the Prostate is advisable.
-
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) The physician will insert a lubricated and gloved finger to the patient’s rectum to figure out any abnormality with the Prostate. Using a hollow and thin needle, a sample tissue from the Prostate is taken and examined by the urologist. Then, it goes for an ultrasound.
- Biopsy The Biopsy is the most authentic test to detect any type of cancer. After the biopsy, a set of antibiotics are given to the patient to avoid further infection. This test will help to understand whether the problematic cells are cancerous or not.
Mainly there are 3 types of biopsies done for these cases:
-
- A transperineal biopsy The biopsy is done by inserting a needle behind the scrotum inside the Prostate; mostly done with general anaesthesia.
-
- A transrectal In the VSG Guided Prostate biopsy, the needle is inserted through the rectum. An ultrasound probe is also inserted through the rectum. This procedure is generally done by local anaesthesia.
- Biopsy during a cystoscopy examination
The Prostate cancer treatment
The necessity and the procedure of the treatment largely depend on the individual patient condition and the stage of cancer. In many cases, if the cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, the patient may not need any sort of treatment at all.
At the later stages, the treatment is done to cure the Prostate Cancer while keeping up the life expediency.
Once the cancer has spread from the Prostate and has already affected the other parts of the body, the aim remains to delaying the symptoms rather than to cure the concern altogether.
Which type of treatment is the best suited for you largely depend on these factors:
- The size and type of the Prostate Cancer
- The patient’s general health condition
- At which stage it has been diagnosed
- Whether it has spread to other body parts or not
Most of the people tend to ignore the early symptoms and see a doctor only when the situation has already gone out of the hand. It is a universal truth for any type of cancer; early detection is the best treatment.
Content Reviewed by – Asian Hospital Medical Editors
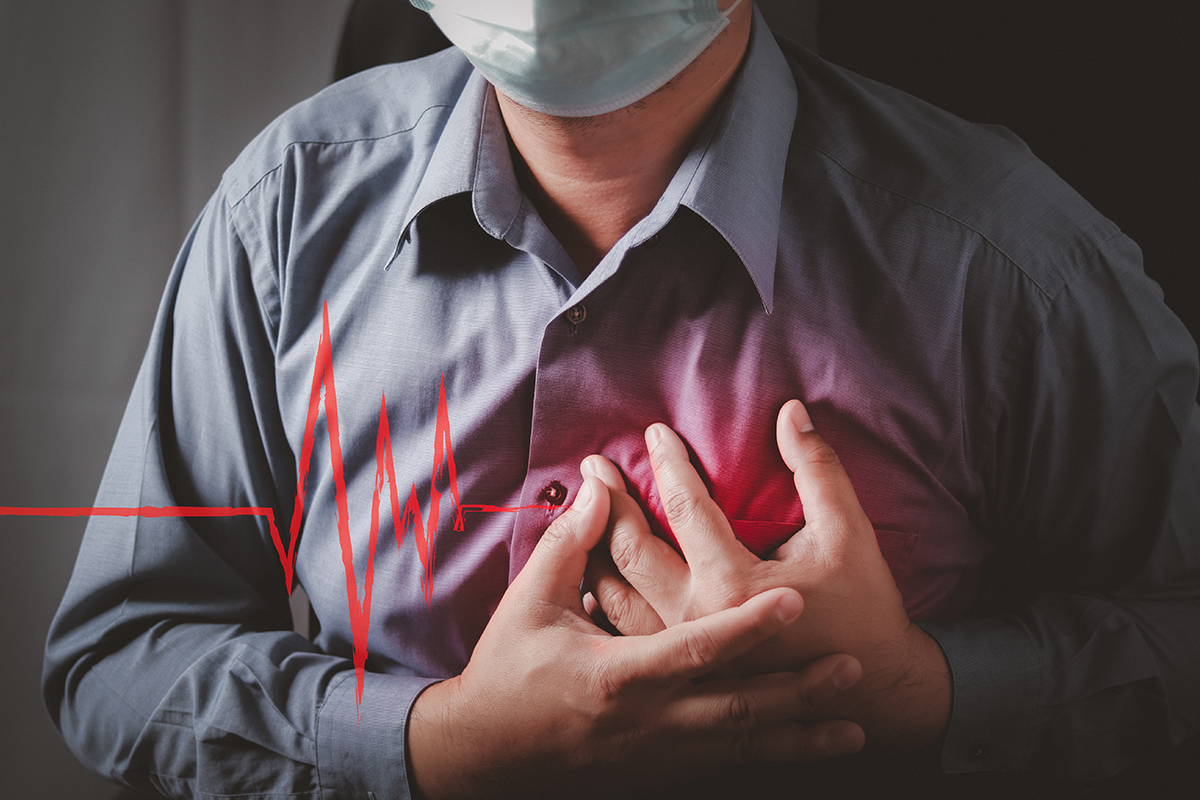
Heart Attack
What is a heart attack? What are the causes of a heart attack?
A heart attack occurs when there is a blockage of blood supply to the heart. The blockage occurs because of the fat and cholesterol build-up. These fatty substances are known as plaques. These plaques create a clot in the coronary arteries, blocking the blood supply. This whole process is known as atherosclerosis.
Moreover, the blood contains oxygen in it. And when this clot occurs, it stops the supply of oxygen-containing blood to the heart and eventually ruptures a heart muscle. This process where the heart lacks oxygen because of the blockage is known as Ischemia. And the rupturing of the heart muscle occurs because of Ischemia. It is known as a heart attack or myocardial infarction (MI).
Other than this, some other causes of a heart attack are not very common. These are-
- Rare medical conditions such as narrowing of the blood vessels can be a cause of heart attack.
- Tears in the coronary arteries can also cause heart attacks.
- When the muscle lining of the blood vessels twitches, it can give rise to a heart attack.
- When a person has either excess or shortage of critical minerals in the body, he might have a heart attack.
- Embolism, or when an air bubble gets inside the coronary arteries and cannot find its way out, causes a heart attack.
What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
Here we are listing the most common symptoms of a heart attack. You must immediately go to a heart hospital if you notice any heart attack symptoms.
- Breathlessness
- Angina Pains: These are chest pains that can be mild to severe. You may feel heaviness and discomfort when going through these angina pains. This pain will start in your chest but slowly and gradually spread to other parts like your arms, waist, or back.
- Sweats
- Rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stomach issues
- Dizziness
- Anxiousness
- Fatigue
- Insomnia before the heart attack.
What is the way to diagnose a heart attack?
Heart attack is a critical condition. Therefore, the doctors treat and diagnose heart attack as an emergency case.
First, the doctors asked a few questions about the family history, lifestyle, and previous medical history. Then, if they think it can be a heart attack, they perform tests to confirm whether or not it is a heart attack.
The doctors do the following tests to determine a heart attack.
- Electrocardiogram or ECG- This is the first test a patient with heart attack symptoms undergo. In this test, the tester attaches electrodes to the person’s chest, arms and legs. Then electrical signals pass through the heart and record the electrical signals as waves.
- A chest X-Ray- This shows the size and state of the heart.
- Echocardiogram or Ultrasound: It can bring moving images of the blood flowing through the heart. It determines the ruptured spot in your heart.
- Troponin Test- This test checks for damage to the heart muscles.
- Cardiac Catheterization is the test in which a catheter, a small tube, goes through your blood vessels. This test allows the doctors to see the plaque build-up around your heart.
What are the risk factors for a heart attack?
Several factors can determine who is at risk for heart attack-
- Diabetic people
- People with a high blood pressure
- Obesity
- Age- For males, being 45 or plus. And for females being 55 or plus.
- Use of drugs like cocaine
- Triglycerides or a higher level of cholesterol in the body
How long does a heart attack last?
The symptoms of a heart attack may occur a long time before the actual episode comes. The real signs and pain can last for a couple of minutes, then they reduce gradually, but they may return.
You must not delay going to a heart hospital as soon as you notice the symptoms. The more you delay, the more time it will last, making the case more critical.
Treatment of a heart attack-
Drugs in the treatment of a heart attack-
If you have a heart attack, you need to take aspirin to prevent your blood from getting thick and causing clotting. Doctors also give antiplatelet drugs to eliminate the clots. To dissolve the blood clots or clot busters present in the arteries.
Inserting of stent-
Doctors insert a stent through a cathedral, a small metal tube. It goes into the artery, which is blocked. These stents have medicines that will prevent the artery from getting blocked again.
Bypass Surgery-
Surgeons perform this major surgery on patients with massive blockage in the arteries. In this particular surgery, the surgeon takes out a vein from your hand, leg, or chest, makes a bypass, and inserts that vein in the artery. This surgery restarts the flow of blood in the artery that is blocked.
Heart Transplant-
The doctors perform a heart transplant for patients whose heart is severely damaged and cannot recover. In this surgery, the surgeons change the damaged heart with another donor’s healthy heart.
How can I prevent a heart attack?
- By eating a balanced and healthy diet.
- No smoking, no drugs.
- Limiting alcohol habits.
- Checking for your blood pressure.
- Controlling diabetes.
- Work out and maintain your weight.
- Reduce your alcohol consumption.
- Manage your stress and anxiety.
- Address your sleeping schedules and insomnia issues.
What to expect after a heart attack?
Your symptoms will ease out slowly and gradually after your treatment begins. Unfortunately, you have to stay for a while in the hospital. Your recovery speed depends on your medicine, and surgery, like bypass surgery, takes longer to recover.
But when you reach home, eat, work and exercise as directed by your doctor.
Heart attacks are not something that you can take lightly. You must check for the signs and to a good cardiologist. We at Asian Institute of Medical Sciences, Faridabad, have the most skillful, experienced, and precise surgeons. That is what makes us the best heart hospital in Faridabad. So book your appointment now, and our expert doctors will cater to all your needs.
Content Reviewed by – Asian Hospital Medical Editors
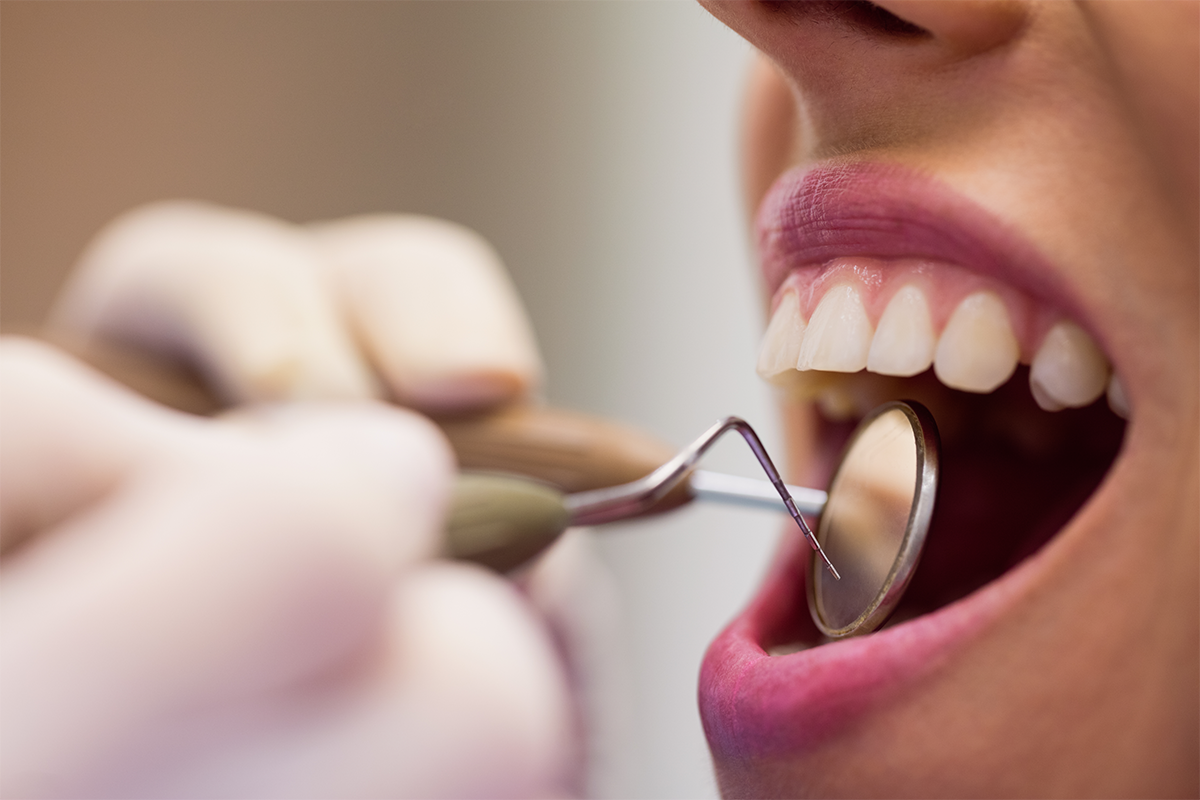
Oral Cancer
Oral Cancer: Everything you need to know about it!
What do you mean by oral cancer?
Oral cancer, also called oral cavity cancer, develops in the parts of the mouth like lips, gums, floor, the roof of the mouth, and the inner lining of the cheeks. Oral cancer also occurs in the oropharynx. This cancer comes in the category of head and mouth cancer.
What happens in oral cancer?
When a person has oral cancer, he has lips and mouth sores. Unfortunately, these sores do not cure. However, doctors can easily cure oral cancer at an early stage. But people ignore the signs and go at a much later stage. Oral cancer is the most common type of head and neck cancer. And if people do not treat it within time, it spreads to the entire mouth, throat, and other parts of the head and neck.
What are the signs and symptoms of oral cancer?
The following are the signs and symptoms of oral cancer-
- Sores in the mouth, tongue, lips, cheek lining, and back of the throat. These soars do not heal with time.
- Change in voice.
- Problems in chewing and swallowing food.
- White or red patches appear in the parts of the mouth.
- Pain in the jaw.
- Swelling in the gums.
- A lump usually forms on the cheek, tongue, or lips.
- Pain in the ear.
- Unexplained loss of weight.
- Loss of teeth.
- Pain around the teeth.
- A problem in moving the tongue and jaw.
- Numbness in the areas of the mouth.
- Bleeding in the mouth.
What causes oral cancer? And what are the risk factors for oral cancer?
Cells on the lips and mouth mutate themselves. These mutations keep growing, and the healthy cells keep dying. And eventually, these cells form a tumor.
There are certain risk factors that can increase the chance of mouth cancers-
- Cigarette and Tobacco- Most patients have oral cancer because of long-term consumption of cigarettes and tobacco. The ones who smoke cigarettes or consume tobacco in the form of snuffs or chewing tobacco are more likely to develop oral cancers. Smoking affects the throat and the mouth. And chewing tobacco affects the cheeks and the gums.
- Gutka or Betel quid- People in India are very fond of gutkas and betel quid. Betel quid is made out of betel nut, lime, and some spices. At the same time, gutka is a blend of tobacco and betel quid. People who chew these two things are at a higher risk of having oral cancer.
- Alcohol- Drinking alcohol in large quantities can irritate the cells. These make the cells susceptive to oral cancer. Therefore, you must balance your drinking habits and consume alcohol within your limits.
- HPV infection: HPV, or Human Papillomavirus infection, is a group of more than a hundred and fifty viruses. These viruses are common in people who have multiple sexual partners. Oral sex is the most common way of spreading HPV. HPV can lead to oral cancer in the tongue and back of the throat.
- Age- Oral cancer can develop at any age. But except for the HPV virus, oral cancers are not very common in younger people. Usually, people above the age of 55 years develop this type of cancer. It is because this cancer takes a lot of time to develop. Therefore, younger people usually do not have it.
- Gender: The chances of getting Oral and oropharyngeal cancers are more common in males than females.
- Weak immunity system and lower nutritional diet- People who have weak immunity and do not eat a balanced diet are also at risk of oral cancer. Therefore, we must have a balanced diet that includes all the essential vitamins, minerals, proteins, and carbs.
- Ultraviolet rays- The UV rays are harmful to us. These rays can assist in causing oral cancer. Oral cancer on the lips is prevalent due to the detrimental effects of ultraviolet rays.
How many stages are there in oral cancer?
There are four stages of oral cancer-
- The first stage- The tumor is not more than two cms in this stage. There is no spread of tumors in the lymph nodes. And the cancer cells look not very different from the normal cells.
- The second stage- The tumor grows in size to about four centimeters long during stage two of oral cancer.
- The third stage- The tumor might be larger than four centimeters during this stage. It may even spread to one of the lymph nodes.
- The fourth stage- The cancer cells look very abnormal during this stage. The tumors can be of any size and spread to tissues, lymph nodes, and other body parts.
How do cancer hospitals treat oral cancer?
Treatment for oral cancer depends on the place of the cancer cells and the stage of cancer. Sometimes doctors even use multiple ways to treat a patient. Therefore, you must visit a cancer hospital and discuss what type of treatment they will give you.
The doctors use the following ways to treat patients with oral cancer-
- Surgery- Surgeries help remove the tumors from the mouth, lymph nodes, and incisions in the neck. Glossectomy is a surgery that wholly or partially removes the tongue from the mouth. Sometimes after extensive surgeries, where the doctors remove the tissues, they also do reconstruction to fill the gaps.
- Radiation- Radiation therapy uses high beams to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is done alone if the patient is in an early stage. Otherwise, doctors use this after surgeries or with chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment makes use of chemicals to kill cancer cells. At times, chemotherapy is also done along with radiation therapy to increase the effects.
- Targeted drug therapy- This therapy uses certain drugs and interferes with the process of cancer cell growth. This treatment is effective in both- the advance and early stages of mouth cancer.
- Immunotherapy- Doctors use this treatment only for patients at a higher stage and other ineffective treatments. In this therapy, the health experts interfere with the immunity system, which otherwise cannot fight the cancer cells.
You must immediately start your treatment if you have any symptoms of oral cancer or even at an early age. Asian Hospital, Faridabad, is not the best for cancer treatment in Faridabad but the best cancer hospital in Asia.
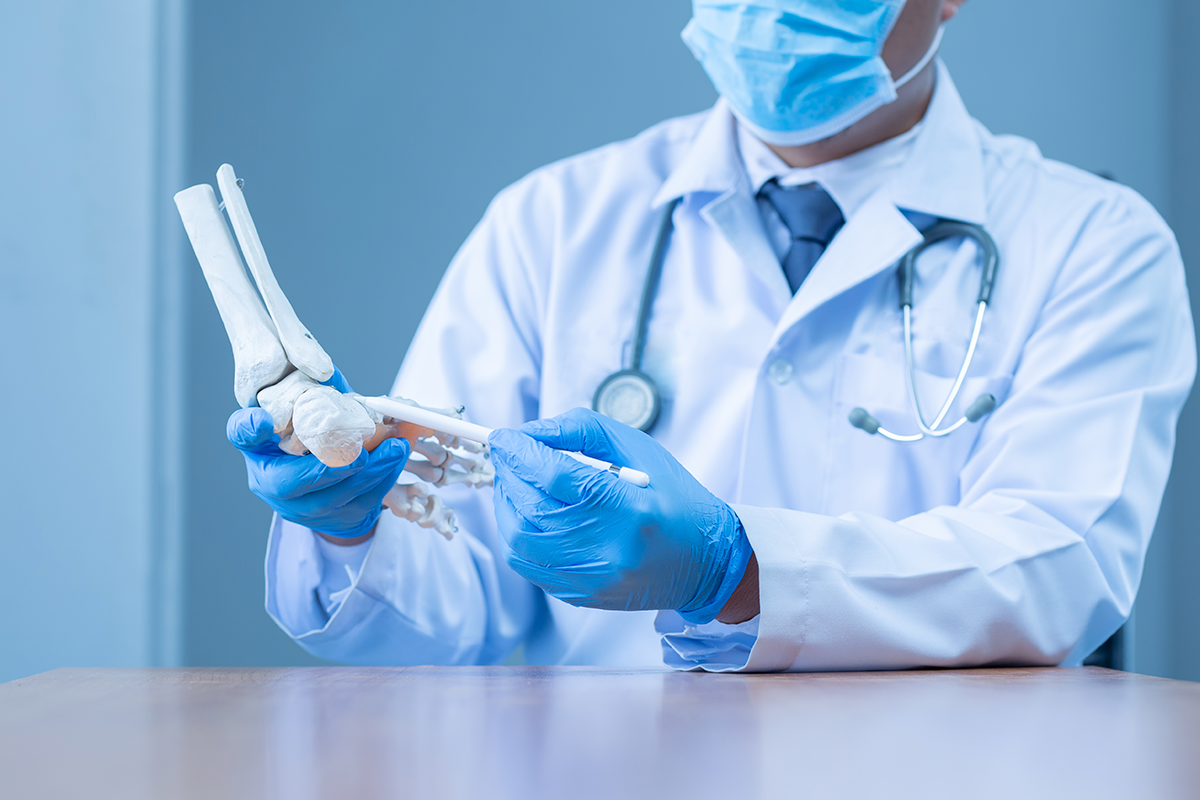
Orthopedics
What is the orthopedics branch in medical science?
Orthopedics is the branch of medical science related to our bones and muscles. It deals with our bodies’ muscles, bones, joints, tendons, and ligaments.
Who is an Orthopedic Doctor?
An Orthopedic doctor is a specialized person skilled in dealing with the Orthopedic branch. They treat the deformities and injuries in our musculoskeletal system. They sometimes perform surgeries but also use other methods to treat the problems.
Orthopedic doctors usually specialize in particular orthopedics such as hand, foot, leg breakage, etc.
For what reasons do people visit orthopedic doctors?
You must go to an orthopedic doctor if you have any of the following problems-
- Broken bones
- Pain in the joints
- Bone tumors
- Backache
- slip disks or ruptured discs
- Spinal Stenosis
- Arthritis
- Hip dysplasia
- Carpal tunnel
- Club foot
- Limb lengthening
- Foot, ankle, and hand injuries
- Achilles’ tendons
- Osteoporosis
- bursitis
- scoliosis
- sports injuries
What non-surgical methods do the Orthopedic Doctors perform?
Every Orthopedic doctor first tries to use non-surgical methods to treat the patient. Then, they only use surgical procedures when no other way can help cure the problem.
These are the non-surgical methods that Orthopedic doctors use-
- Medications- Orthopedic doctors prescribe medicines if the patient complains of pain. They also give medication for swelling and drugs to reduce inflammation.
- Physical Exercises- Your doctor might also suggest you do some exercises for you. These exercises, if done in the correct motion, will help you lose your rigidness.
- Lifestyle changes- Your doctor may suggest some changes in your lifestyle. They may ask you to add or remove certain things from your diet and give you workout tips. Ask you to sit in a certain posture and so on.
What type of surgeries do Orthopedic Surgeons perform?
An Orthopedic doctor has to perform various surgeries depending on the patient’s problem.
Here are the most common types of surgeries that orthopedists use to treat patients-
- ACL reconstruction surgery- Anterior Cruciate Ligament surgery is the most common type of surgery that orthopedist surgeons use to cure the knee. Usually, athletes and sports players damage their ACL while playing. Therefore, ACL surgery is highly beneficial for them.
- Knee Replacement Surgery- Sometimes, the patient gets more hurt and requires either a partial or complete knee replacement. In a partial knee replacement, the doctors remove the wounded part of the knee and substitute it with new metal. In a total knee replacement, the orthopedics have to remove the entire knee and replace it with new metal parts.
- Ankle repair- A patient’s ankle joint is not steady after a fracture. His bones might not adjust like before, even after the medical treatment. So, the orthopedic doctors perform this surgery to make the ankle normal like earlier.
- Spinal Surgeries- Though medicines can cure most back problems, at times, the person might be very old or have hurt their back too severely. These are the people who require spinal surgery. Otherwise, it can cause problems in other parts, such as the legs.
- Joint fusion- During this surgery, the surgeons remove the problem-causing cartilage and weld the two bones together. The joining of the two bones provides more stability to the joint.
How do Orthopedic doctors diagnose the problems?
To diagnose the problems of the patient, the Orthopedic doctors follow the following procedures-
- First and foremost, they ask about the person’s symptoms, their problem, and the parts in which they feel the pain and issues.
- Then they ask more questions about the person’s previous medical history, wounds, physical activities, etc.
- After this, they examine the patient physically. For example, they may move and touch the part that hurts. They might also check for swelling.
- The Orthopedic doctors might also ask the person to get some tests done such as X-rays, MRI scans, bone scans, ultrasounds, or blood tests. These tests help the Orthopedists get a clearer picture of the injury or the hurting part.
Bones and ligaments are very fragile. Therefore, the Orthopedist must handle the problems in these parts with precision and care. Hence, it would be best if you only went to the best orthopedic doctor with experience and accuracy in his field.
You can find the most suitable orthopedic doctor in Faridabad with us at the Asian Institute of Medical Sciences, Faridabad. Our orthopedists have years of experience in their respective fields. With their experience and expertise, our doctors treat the patients with care and accuracy and handle the cases calmly.
Content Reviewed by – Asian Hospital Medical Editors
 Appointment
Appointment  Lab Report
Lab Report Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor  Health/Lab Packages
Health/Lab Packages