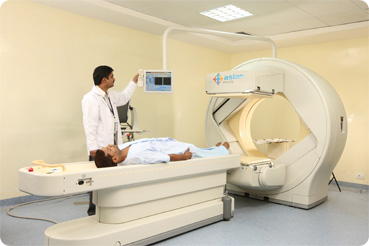
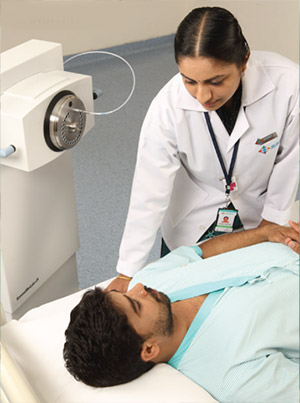
Radiation Oncology
Radiotherapy is the controlled use of high energy X-rays to treat different types of cancer. It is also known as radiation oncology treatment (Cancer Treatment). According to NCI, approximately 60% of the cancer patients receive radiation therapy during treatment and in some cases; radiotherapy is also used to treat benign (non-cancerous) tumours.
Radiation therapy is done with curative intent or palliative intent and usually lasts from one week to 7-8 weeks. The duration depends on stage, histological type, location and intent of treatment. Radiation therapy is a local treatment like surgery. It can be done alone or in combination with other modalities like surgery and/or chemotherapy. It can be implemented to cure tumour, shrink the tumour prior to radical surgery in pre-operational setting and post operation to kill microscopic amounts of leftover tumours and to prevent relapse.
 Uses of Radiotherapy
Uses of Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy may be used:
- to cure an illness – for example, by destroying a tumor (abnormal tissue)
- to control symptoms – for example, to relieve pain
- before surgery – to shrink a tumor to make it easier to remove
- after surgery – to destroy small amounts of leftover tumor and to prevent relapse
Courses of Radiation
Radiotherapy is usually given as a course of treatment that lasts for a number of days or weeks. Most people who undergo radiotherapy to treat a serious condition, such as cancer, have five treatments a week (one treatment a day, Monday to Friday) with a break at the weekend. Taking a break allows the normal and non-cancerous cells to recover. Depending on cases, a patient can get radiation treatment more than once a day or over the weekend.
 Appointment
Appointment  Lab Report
Lab Report Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor  Health/Lab Packages
Health/Lab Packages